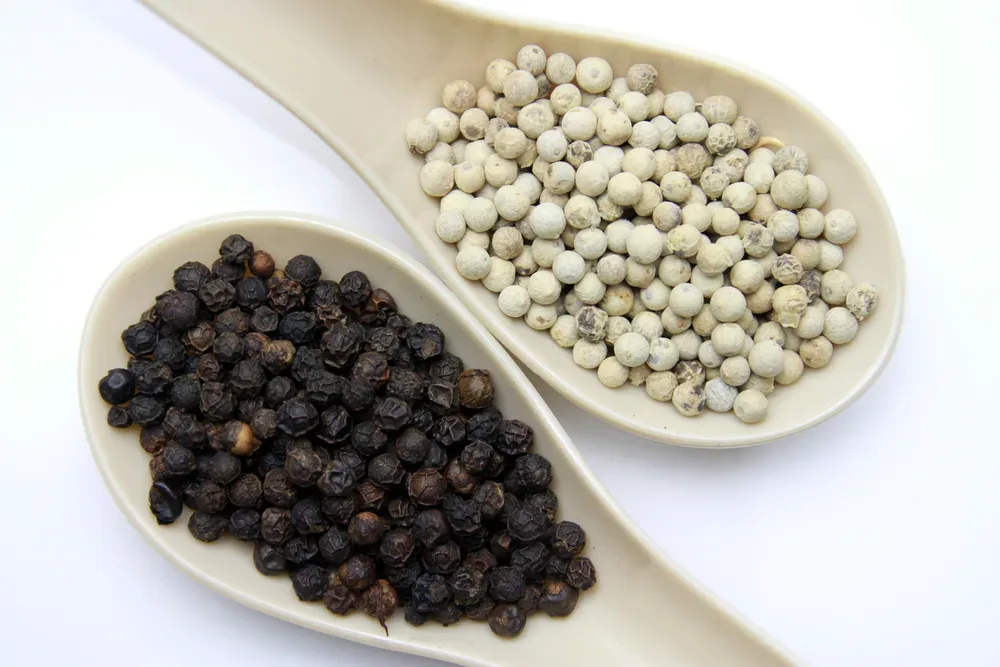
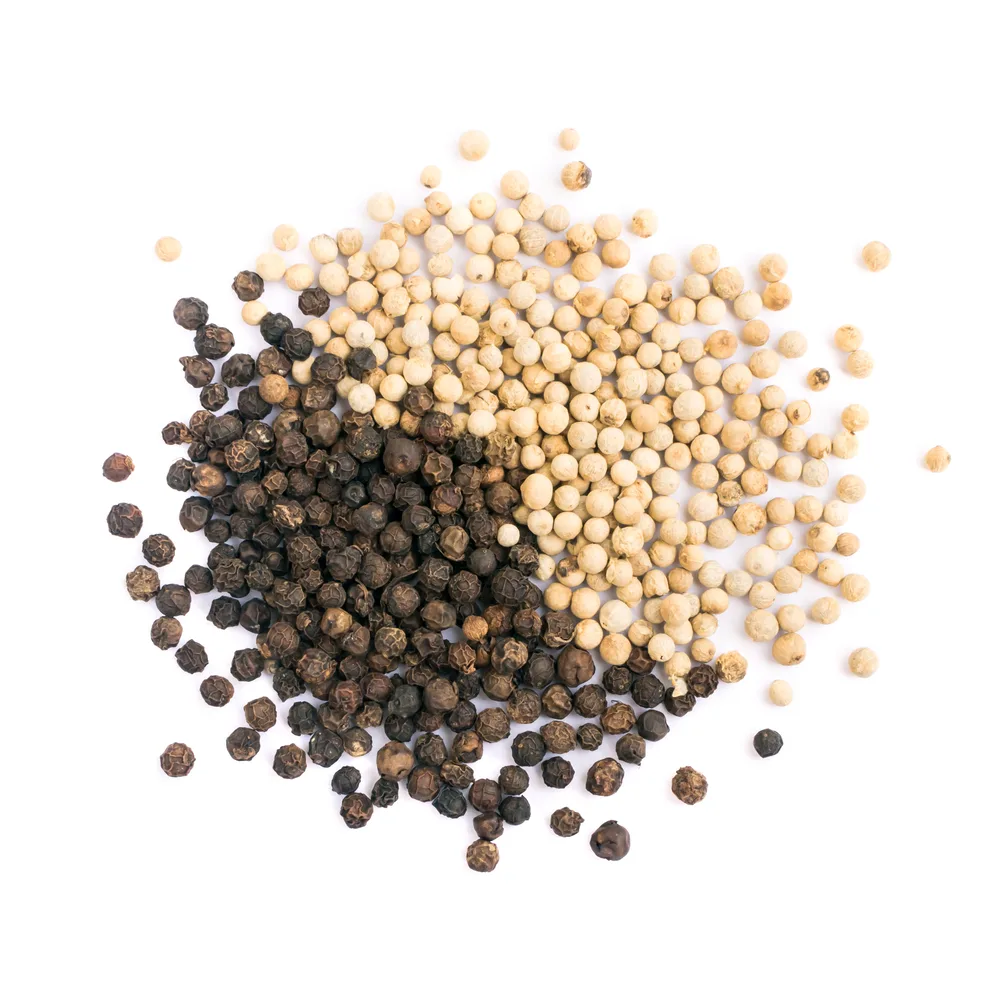
Did you know that the most widely used spice in the world pepper exists in two distinct forms with remarkably different characteristics? Both white pepper and black pepper originate from the same plant, Piper nigrum, yet their processing, flavour profiles, and culinary applications set them apart.
Kerala, India often hailed as the “Land of Spices” is home to some of the finest Kerala spices, cherished globally for their superior quality. In this guide, we delve into the nuanced differences between white pepper vs black pepper, exploring their unique attributes, health benefits, and best culinary uses.
What is White Pepper?
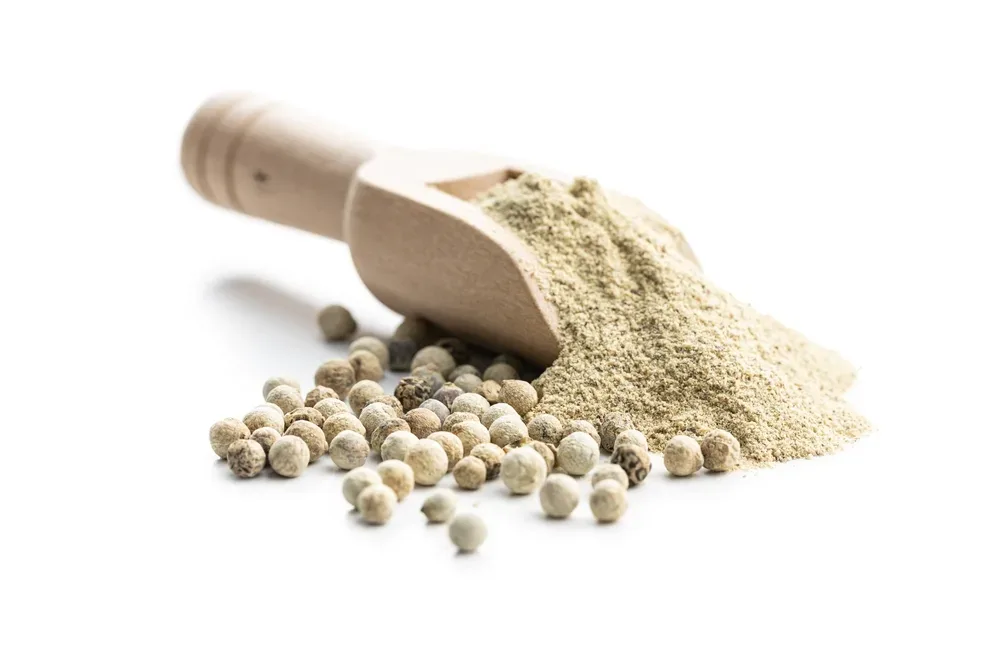

White pepper is extracted from mature Piper nigrum berries that undergo specific soaking and fermentation steps to strip off their outer skin. Smooth off-white peppercorns develop an earthy taste because of the extraction process, which makes white pepper suitable for light-coloured dishes that require a refined spicing element.
Gourmets in culinary arts use white pepper because of its gentle spiciness along with refined scents to enhance creamy sauces and Asian recipes as well as soups. Discover superior gastronomic possibilities through the acquisition of Best Kerala White Pepper.
Unveiling our latest blog: What is White Pepper? Discover its unique flavor, health benefits, and how it elevates your dishes! Read now!
What is Black Pepper?
Black pepper requires unripe berries to produce its product through sun drying which leads to the development of dark wrinkled skins. Due to drying methods, the berries develop a robust spicy flavour, which contains piperine as its spice heat-planting compound.
Black pepper stands as a culinary delight, which American chefs and global cooks use to improve grilled meats and roasted vegetables and zesty marinades. Additional information on the intense spiciness comparison appears in “White Pepper vs. Black Pepper: Which Is the Hottest Spice?”
Appearance: A Visual Distinction
The easiest way to differentiate between these two spices is by their peppercorn appearance:
- Black Peppercorns: Dark, wrinkled, and slightly rough due to the drying process.
- White Peppercorns: Smooth, off-white or beige, with a refined look due to skin removal.
These visual differences make white pepper a preferred choice for elegant, light-hued dishes, where specks of black pepper might be undesirable.
Flavour Profile: Subtle vs. Bold
When it comes to pepper flavour, the contrast is striking:
- Black Pepper – Intensely pungent, with a sharp, lingering heat due to its high piperine content.
- White Pepper – Earthier and milder, with a hint of fermentation resulting from the soaking process.
Since white pepper undergoes extended soaking, it develops a more complex aroma, making it a sophisticated choice for refined palates.
Culinary Uses: Where Each Spice Shines
Both white pepper and black pepper bring distinct magic to different cuisines:
- White Pepper – Ideal for creamy sauces, mashed potatoes, seafood, and Asian soups, where a seamless blend of flavours is desired.
- Black Pepper – A staple in bold, spice-forward dishes like steaks, stir-fries, and rich gravies.
Both spices are incredibly versatile, offering endless possibilities in cooking with pepper in the kitchen. Looking to stock up on premium quality pepper? Check out white pepper buy online.
Health Benefits: More than Just a Spice
Beyond their culinary excellence, both varieties of pepper offer impressive pepper health benefits:
- Rich in Piperine – A potent antioxidant known to enhance nutrient absorption and boost metabolism.
- Digestive Aid – Stimulates enzyme production, promoting better digestion and gut health.
These spice nutrition benefits make pepper a valuable addition to any diet, not just for its flavour but also for its health-enhancing properties.
Buying and Storing: Preserving Freshness
To ensure maximum potency and flavour, follow these essential spice storage tips, Always opt for whole peppercorns over pre-ground varieties for longer shelf life. Store in airtight containers, away from light and moisture, to prevent flavour loss. Whole black pepper retains its freshness longer than white pepper, especially when ground. For the best quality Kerala spices, always choose trusted sources that offer superior aroma and freshness.
White Pepper vs. Black Pepper: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | White Pepper | Black Pepper |
| Origin | Fully Ripened Berries Of Piper Nigrum | Unripe Berried Of Piper Nigrum |
| Processing | Socked & Fermented To Remove The Outer Skin | Sun Dried, Causing The Outer Layer To Blacken |
| Flavour | Mild Earthy, With Subtle Fermentation Notes | Bold Spicy And Pungent |
| Piperine Content | Lower Due To Skin Removal | Higher Resulting In Stronger Heat |
| Best For | Light Coloured Dishes Creamy Soups Delicate Sauces | Spice Forward Dishes, Grilled Meats, Bold Flavours |
| Appearance | Pale, Smooth, Uniform In Color | Dark, Wrinkled, Coarse Texture |
| Shelf Life | Shorter, Especially When Ground | Longer-Last Ing, Particularly In Whole Form |
| Health Benefits | Supports Digestion, Anti-Inflammatory Properties | Enhances Metabolism, Antioxidant -Rich |
Final Verdict: Which One Should You Choose?
Personal food preferences and culinary requirements determine which pepper variety you will choose between black and white. The delicate earthy taste becomes noticeable through white pepper, which works best for light-hued preparations. Those seeking intense spicy flavours or textured dishes should choose black pepper if they want to achieve their desired effect.
Black pepper and white pepper maintain distinct roles around the world so they deliver both unique taste sensations while benefiting human health. Bits of restaurant success demand authentic high-quality Kerala spices as your selection source to transform your cooking into extraordinary masterpieces.


